网络套接字
1. 网络编程概念
1.1 IP地址和端口号
数据实际是由进程产生和接收的,IP确定了主机,但还要进一步确定主机上的网络进程。网络通信的本质就是跨网络的两台主机之间的进程间通信。
| 概念 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| IP | IP地址唯一的标识了互联网中的一台主机。 |
| 端口 | 端口号唯一地标识主机上的一个网络进程。 |
源端口号确定源主机上的网络进程,目的端口号确定目的主机上的网络进程。
IP和端口就能标识互联网上的唯一一台机器上的唯一一个进程。
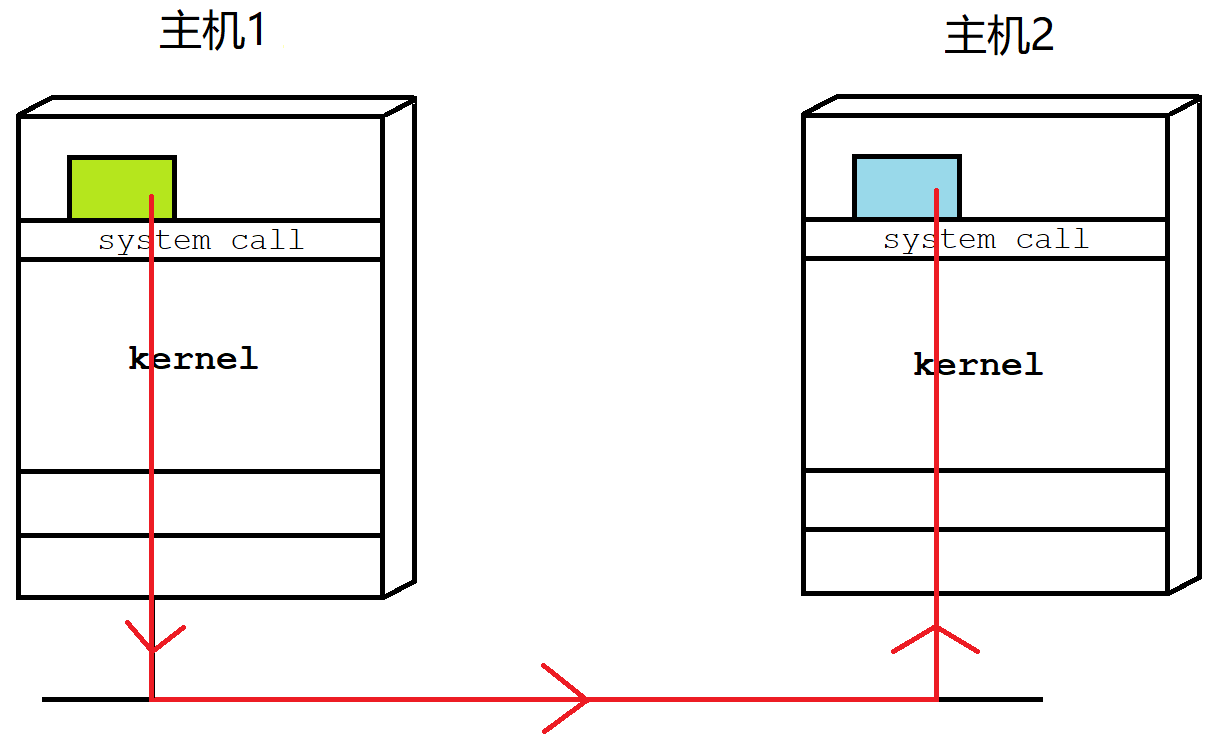
可以把整个网络看作是一个大操作系统,所有的网络行为就可看作是这个系统内的进程间通信。
进程具有独立性,进程间通信的前提是先让不同的进程看到同一份资源,而网络通信的临界资源就是网络。
1.2 理解网络字节序
当跨主机传输数据时,必须考虑且强制规定字节序。规定:网络中的数据一律都采用大端的形式。
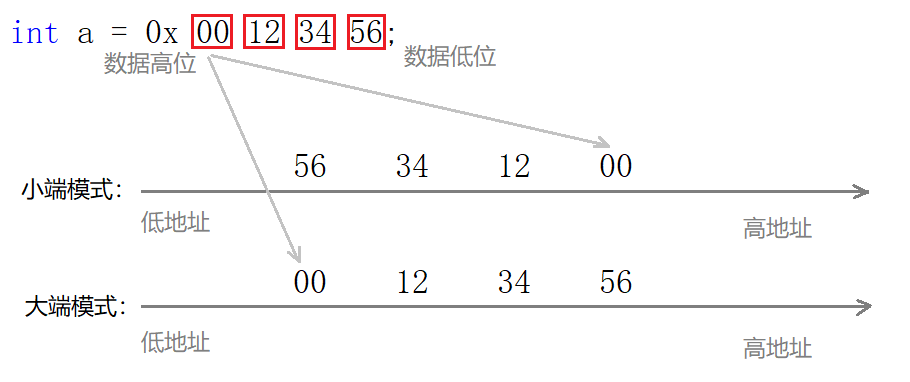
一般从低到高地将数据发出,所以接收时也是先收到低地址数据,便于存储。
所以系统提供了库函数,可将数据进行主机和网络字节序的转化,如下:
#include <arpa/inet.h>
uint32_t htonl(uint32_t hostlong); // 主机 转 网络 长整型
uint16_t htons(uint16_t hostshort); // 主机 转 网络 短整型
uint32_t ntohl(uint32_t netlong); // 网络 转 主机 长整型
uint16_t ntohs(uint16_t netshort); // 网络 转 主机 短整型1.3 sockaddr结构体
通信方式有很多种,比如TCP/IP属于是AF_INET,域间套接字属于AF_UNIX。各家协议都有自己的套接字结构体。
接口设计者提供一个通用结构体叫sockaddr。各种结构体可以强转成sockaddr,接口内部可以通过前16位数据判断具体协议类型。
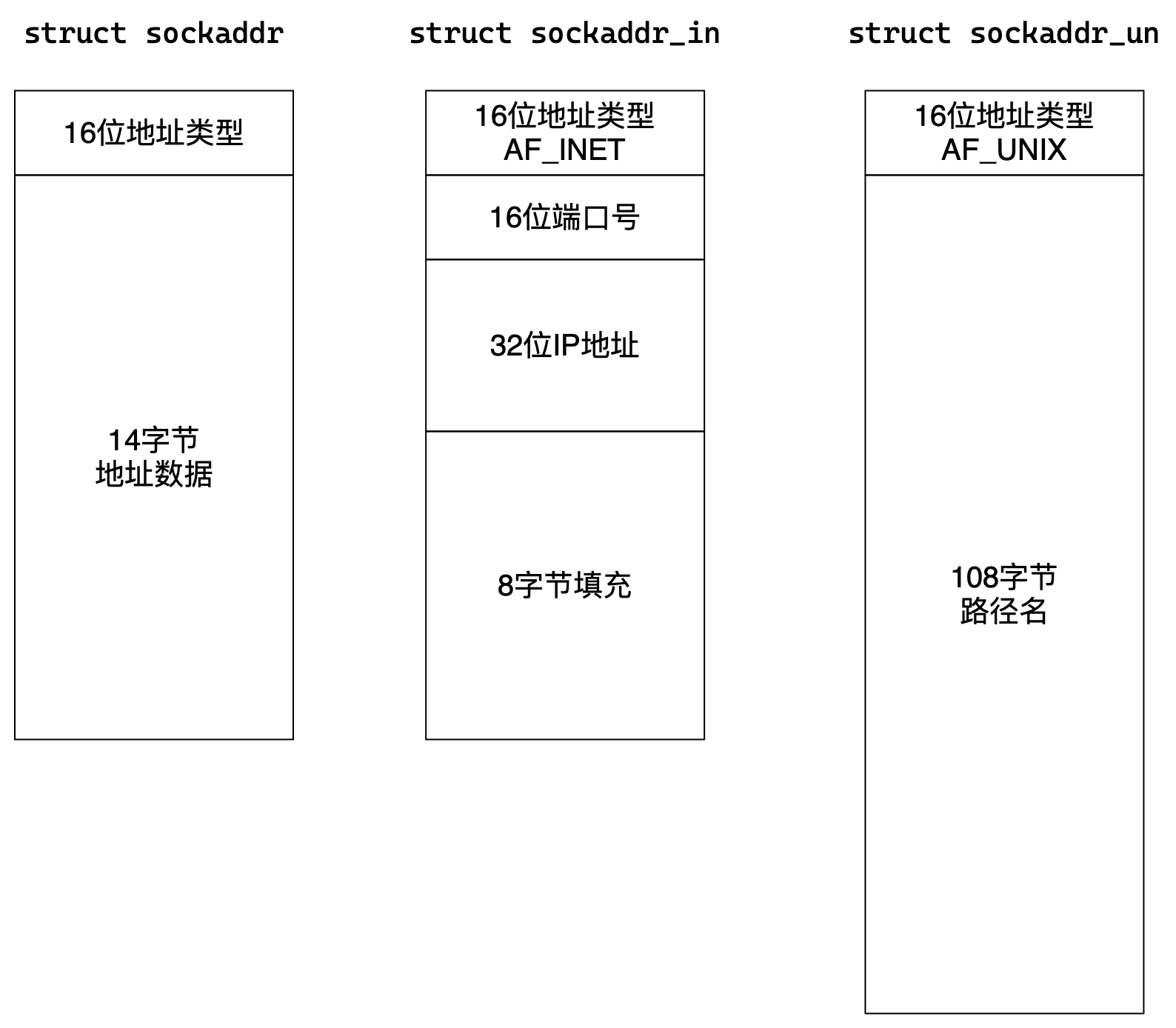
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <apra/inet.h>
#define __SOCKADDR_COMMON(sa_prefix) \
sa_family_t sa_prefix##family // sa_family_t(unsigned short) sin_family
typedef uint16_t in_port_t; // 端口类型
typedef uint_32_t in_addr_t; // IP 类型
struct in_addr
{
in_addr_t s_addr;
};
/* Structure describing an Internet socket address. */
struct sockaddr_in
{
__SOCKADDR_COMMON (sin_); /* Protocol Family. */
in_port_t sin_port; /* Port number. */
struct in_addr sin_addr; /* Internet address. */
/* Pad to size of `struct sockaddr'. */
unsigned char sin_zero[sizeof (struct sockaddr) -
__SOCKADDR_COMMON_SIZE -
sizeof (in_port_t) -
sizeof (struct in_addr)];
};
2. 网络编程接口
2.1 通用接口
| 接口 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| socket() | 创建套接字本质就是打开文件,与网络无关。 |
| bind() | 本质是将IP端口和套接字文件关联。 |
socket
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
//1. 创建套接字
int socket(int domain, int type, int protocol);| 参数 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| domain | 指定通信方式的协议家族,TCP/UDP使用AF_INET即可 |
| type | 指定通信协议,UDP传SOCK_DGRAM,TCP传SOCK_STREAM |
| protocol | TCP/UDP统一传0 |
| 返回值 | 调用成功返回网络套接字文件的文件描述符,调用失败返回负值。 |
int sock = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_DGRAM, 0);
if (sock < 0) {
std::cerr << "socket error: " << errno << std::endl;
exit(1);
}bind(server)
//2. 绑定IP端口
int bind(int socket, const struct sockaddr *address, socklen_t address_len);建立网络连接需要确定IP和端口,但云服务器不允许绑定固有IP,使用INADDR_ANY让系统自动绑定。
客户端不需要显式绑定,系统自行分配端口号冲突。
首次发送数据的时候会自动绑定。
| 参数 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| socket | socket接口的返回值 |
| address | 套接字信息结构体地址和长度,用来指定机器相关的套接字信息 |
| 返回值 | 返回值成功返回0,失败返回–1 |
struct sockaddr_in local;
local.sin_family = AF_INET; // 协议家族
local.sin_port = htons(port); // 端口
local.sin_addr.s_addr = INADDR_ANY; // IP地址由系统决定,用于云服务器
local.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(_ip.c_str()); // 将点分十进制的IP串转化成32位整数并改为大端序列
if (bind(sock, (struct sockaddr*)&local, sizeof(local)) < 0) {
std::cerr << "bind error: " << errno << std::endl;
exit(1);
}close
int close(int fd);关闭套接字文件,系统层面是释放文件资源,网络层面是TCP四次挥手。
2.2 UDP接口
recvfrom
#include <sys/socket.h>
ssize_t recvfrom(int socket,
void *restrict buffer, size_t length,
int flags,
struct sockaddr *restrict address, socklen_t *restrict address_len);| 参数 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| socket | 网络套接字的文件描述符 |
| buffer / length | 接收数据的接受缓冲区 / 缓冲区的长度 |
| flags | 接收数据的方式默认为0 |
| address / addrlen | 发送者的套接字结构体的地址 / 长度 |
| 返回值 | 实际接收的字符个数 |
struct sockaddr_in peer;
socklen_t len = sizeof(peer);
ssize_t s = recvfrom(sock, buf, sizeof(buf)-1, 0, (struct sockaddr*)&peer, &len);
if (s > 0) {
buf[s] = 0;
std::cout << "server # " << std::endl << buf << std::endl;
}
else
std::cerr << "recvfrom error" << std::endl;sendto
#include <sys/socket.h>
ssize_t sendto((int socket,
const void *message, size_t length,
int flags,
const struct sockaddr *dest_addr, socklen_t dest_len);| 参数 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| socket | 网络套接字的文件描述符 |
| message / length | 发送字符数组的地址 / 数组的长度 |
| flags | 发送数据的方式默认为0 |
| address / addrlen | 接受者的套接字结构体地址 / 长度 |
| 返回值 | 实际发送的字符个数 |
//server
s = sendto(_sock, buf, strlen(buf), 0, (struct sockaddr*)&peer, len);
//client
struct sockaddr_in server;
server.sin_family = AF_INET;
server.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(_sip.c_str());
server.sin_port = htons(_sport);
ssize_t s = sendto(_sock, msg.c_str(), msg.size(), 0, (sockaddr*)&server, sizeof(server));2.3 TCP接口
listen
//3. 开始监听 TCP server
int listen(int socket, int backlog);TCP是面向连接的通信协议,所以在通信前需先建立连接。
listen的本质是设置套接字为listen监听状态,允许用户进行连接。
accept
//4. 接收请求 TCP server
int accept(int sockfd, struct sockaddr *addr, socklen_t *addrlen);**accept表示正式建立与客户端的连接。**本质阻塞式的等待三次握手完成,并将连接提取到应用层。
socket返回的sock_fd用来监听连接。accept返回的sock_fd是用来通信的fd。
connect (client)
//5. 建立连接 TCP client
int connect(int sockfd, const struct sockaddr *addr, socklen_t addrlen);**connect的作用是主动向服务端发起连接。**本质是向服务器端发起TCP的三次握手,并等待握手完成。
recv/send
ssize_t recv(int sockfd, void *buf, size_t len, int flags);
ssize_t send(int sockfd, const void *buf, size_t len, int flags);
ssize_t read(int fildes, void *buf, size_t nbyte);
ssize_t write(int fildes, const void *buf, size_t nbyte);网络数据收发接口,本质是读写文件。
TCP协议是流式套接字,TCP收发接口和文件读写非常像,仅多了方式参数flags。
2.4 IP格式转换接口
// 字符串IP 转 网络整数IP
in_addr_t inet_addr(const char *cp);
in_addr_t inet_network(const char *cp);
int inet_aton(const char *cp, struct in_addr *inp);
int inet_pton(int af, const char *src, void *dst);
// 网络整数IP 转 字符串IP
char* inet_ntoa(struct in_addr in); // 非线程安全
const char *inet_ntop(int af, const void *src, char *dst, socklen_t size);2.5 套接字接口封装
namespace inet {
struct api {
enum {
udp = SOCK_DGRAM,
tcp = SOCK_STREAM,
};
static int Socket(int proto) {
int fd = socket(AF_INET, proto, 0);
if (fd < 0) throw std::runtime_error("socket failed");
return fd;
}
static void Bind(int sock, const std::string& ip, uint16_t port) {
struct sockaddr_in local;
memset(&local, 0, sizeof(local));
local.sin_family = AF_INET;
local.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(ip.c_str());
local.sin_port = htons(port);
if (bind(sock, (struct sockaddr*)&local, sizeof(local)) < 0)
throw std::runtime_error("bind error");
}
static void Bind(int sock, uint16_t port) {
struct sockaddr_in local;
memset(&local, 0, sizeof(local));
local.sin_family = AF_INET;
local.sin_addr.s_addr = INADDR_ANY;
local.sin_port = htons(port);
if (bind(sock, (struct sockaddr*)&local, sizeof(local)) < 0)
throw std::runtime_error("bind error");
}
static void Listen(int sock, int backlog) {
if (listen(sock, backlog) < 0)
throw std::runtime_error("listen error");
}
static void Connect(int sock, const std::string& ip, uint16_t port, int trytime = 1) {
struct sockaddr_in peer;
memset(&peer, 0, sizeof(peer));
peer.sin_family = AF_INET;
peer.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(ip.c_str());
peer.sin_port = htons(port);
while (trytime-- > 0 && connect(sock, (struct sockaddr*)&peer, sizeof(peer)) < 0) {
if (trytime == 0) throw std::runtime_error("connect failed");
sleep(1);
}
}
static int Accept(int sock, std::string* ip = nullptr, uint16_t* port = nullptr) {
struct sockaddr_in peer;
socklen_t len = sizeof(peer);
memset(&peer, 0, len);
int fd = accept(sock, (struct sockaddr*)&peer, &len);
if (ip) *ip = inet_ntoa(peer.sin_addr);
if (port) *port = ntohs(peer.sin_port);
return fd;
}
static int Recv(int sock, std::string* msg, size_t len) {
msg->clear();
std::unique_ptr<char[]> buf(new char[len]{0});
ssize_t s = recv(sock, buf.get(), len, 0);
if (s > 0) {
buf[s] = 0;
*msg = buf.get();
}
return s;
}
static int Send(int sock, const std::string& msg) {
return send(sock, msg.c_str(), msg.size(), 0);
}
static int Recvfrom(int sock, std::string* msg, size_t len,
std::string* ip = nullptr, uint16_t* port = nullptr) {
msg->clear();
std::unique_ptr<char[]> buf(new char[len]{0});
struct sockaddr_in peer;
socklen_t sklen = sizeof(peer);
memset(&peer, 0, sklen);
ssize_t s = recvfrom(sock, buf.get(), len, 0, (struct sockaddr*)&peer, &sklen);
if (s > 0) {
buf[s] = 0;
*msg = buf.get();
}
if (ip) *ip = inet_ntoa(peer.sin_addr);
if (port) *port = ntohs(peer.sin_port);
return s;
}
static int Sendto(int sock, const std::string& msg,
const std::string& ip, uint16_t port) {
struct sockaddr_in peer;
memset(&peer, 0, sizeof(peer));
peer.sin_family = AF_INET;
peer.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(ip.c_str());
peer.sin_port = htons(port);
ssize_t s =
sendto(sock, msg.c_str(), msg.size(), 0, (struct sockaddr*)&peer, sizeof(peer));
return s;
}
};
namespace tcp {
class server {
public:
server(uint16_t port, int backlog = 12) : _sock(0), _port(port), _backlog(backlog) {
init();
}
server(const std::string& ip, uint16_t port, int backlog = 12)
: _sock(0), _ip(ip), _port(port), _backlog(backlog) {
init();
}
int accept(std::string* cip = nullptr, uint16_t* cport = nullptr) {
Accept(_sock, cip, cport);
}
int recv(int sock, std::string* msg, size_t len) {
return inet::api::Recv(sock, msg, len);
}
int send(int sock, const std::string& msg) {
return inet::api::Send(sock, msg);
}
~server() { close(_sock); }
private:
void init() {
_sock = inet::api::Socket(inet::api::tcp);
if (_ip.empty()) inet::api::Bind(_sock, _port);
else inet::api::Bind(_sock, _ip, _port);
inet::api::Listen(_sock, _backlog);
}
protected:
int _sock;
std::string _ip;
uint16_t _port;
int _backlog;
};
class client
{
public:
client(const std::string& svr_ip, uint16_t svr_port, int trytime = 1)
: _sock(0), _sip(svr_ip), _sport(svr_port), _trytime(trytime) {
_sock = inet::api::Socket(inet::api::tcp);
inet::api::Connect(_sock, _sip, _sport, _trytime);
}
int send(const std::string& msg) { return inet::api::Send(_sock, msg); }
int send(int sock, const std::string& msg) { return inet::api::Send(sock, msg); }
int recv(std::string* msg, size_t len) { return inet::api::Recv(_sock, msg, len); }
int recv(int sock, std::string* msg, size_t len)
{ return inet::api::Recv(sock, msg, len); }
~client() { close(_sock); }
protected:
int _sock;
std::string _sip;
uint16_t _sport;
int _trytime;
};
}
namespace udp {
class server {
public:
server(uint16_t port) : _sock(0), _port(port) {
init();
}
server(const std::string& ip, uint16_t port) : _sock(0), _ip(ip), _port(port) {
init();
}
int sendto(const std::string& msg, const std::string& cip, uint16_t cport) {
return inet::api::Sendto(_sock, msg, cip, cport);
}
int recvfrom(std::string* msg, size_t len,
std::string* cip = nullptr, uint16_t* cport = nullptr) {
return inet::api::Recvfrom(_sock, msg, len, cip, cport);
}
~server() { close(_sock); }
private:
void init() {
_sock = inet::api::Socket(inet::api::udp);
if (_ip.empty()) inet::api::Bind(_sock, _port);
else inet::api::Bind(_sock, _ip, _port);
}
protected:
int _sock;
std::string _ip;
uint16_t _port;
};
class client {
public:
client(const std::string& svr_ip, uint16_t svr_port)
: _sock(0), _sip(svr_ip), _sport(svr_port) {
_sock = inet::api::Socket(inet::api::udp);
}
int sendto(const std::string& msg)
{ return inet::api::Sendto(_sock, msg, _sip, _sport); }
int recvfrom(std::string* msg, size_t len)
{ return inet::api::Recvfrom(_sock, msg, len); }
~client() { close(_sock); }
protected:
int _sock;
std::string _sip;
uint16_t _sport;
};
}
}
3. 网络通信设计
3.1 UDP通信
UDP客户端
class udp_client
{
public:
udp_client(std::string sip, uint16_t sport) : _sock(0), _sip(sip), _sport(sport)
{}
~udp_client() {
close(_sock);
_sender.join();
_recver.join();
}
void init() {
_sock = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_DGRAM, 0);
if (_sock < 0) exit(SOCKET_ERR);
_sender = std::thread(&udp_client::send, this);
_recver = std::thread(&udp_client::recv, this);
}
void send()
{
struct sockaddr_in peer;
peer.sin_family = AF_INET;
peer.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(_sip.c_str());
peer.sin_port = htons(_sport);
while (true)
{
std::string msg;
std::cout << "please input:> ";
getline(std::cin, msg);
sendto(_sock, msg.c_str(), msg.size(), 0, (struct sockaddr*)&peer, sizeof(peer));
}
}
void recv()
{
while (true)
{
char buf[1024] = {0};
struct sockaddr_in tmp;
socklen_t len = sizeof(tmp);
ssize_t s = recvfrom(_sock, buf, sizeof(buf), 0, (struct sockaddr*)&tmp, &len);
if (s > 0) buf[s] = 0;
else continue;
std::cout << "server return# " << buf << std::endl;
}
}
private:
int _sock;
std::string _sip;
uint16_t _sport;
std::thread _sender;
std::thread _recver;
};UDP服务端
class udp_server
{
public:
udp_server(uint16_t port) : _sock(0), _port(port)
{}
~udp_server()
{
close(_sock);
}
void init()
{
_sock = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_DGRAM, 0);
if (_sock < 0) exit(SOCKET_ERR);
struct sockaddr_in local;
local.sin_family = AF_INET;
local.sin_addr.s_addr = INADDR_ANY;
local.sin_port = htons(_port);
if (bind(_sock, (struct sockaddr*)&local, sizeof(local)) < 0)
exit(BIND_ERR);
}
void start()
{
char buf[1024] = {0};
while (true)
{
struct sockaddr_in peer;
socklen_t len = sizeof(peer);
ssize_t s = recvfrom(_sock, buf, sizeof(buf), 0, (struct sockaddr*)&peer, &len);
if (s > 0) buf[s] = 0;
else continue;
std::string cip = inet_ntoa(peer.sin_addr);
uint16_t cport = ntohs(peer.sin_port);
std::cout << '[' << cip << ':' << cport << "] " << buf << std::endl;;
std::string rsp = buf;
sendto(_sock, rsp.c_str(), rsp.size(), 0, (struct sockaddr*)&peer, sizeof(peer));
}
}
private:
int _sock;
uint16_t _port;
};3.2 TCP通信
TCP客户端
class tcp_client
{
public:
tcp_client(std::string sip, uint16_t sport) : _sock(0), _sip(sip), _sport(sport)
{}
~tcp_client()
{
close(_sock);
}
void init()
{
// 1. socket
_sock = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
if (_sock < 0)
{
std::cerr << "socket error" << std::endl;
exit(SOCKET_ERR);
}
std::cout << "socket success " << _sock << std::endl;
// 2. connect
struct sockaddr_in peer;
memset(&peer, 0, sizeof(peer));
peer.sin_family = AF_INET;
peer.sin_port = htons(_sport);
inet_aton(_sip.c_str(), &peer.sin_addr);
int cnt = 5;
while (connect(_sock, (struct sockaddr*)&peer, sizeof(peer)) < 0)
{
std::cerr << "connect failed, remaining try " << cnt-- << std::endl;
if (cnt == 0)
{
std::cerr << "connect error" << std::endl;
exit(CONNECT_ERR);
}
sleep(1);
}
std::cout << "connect success" << std::endl;
}
void start()
{
while (true)
{
std::string msg;
std::cout << "please input:> ";
getline(std::cin, msg);
send(_sock, msg.c_str(), msg.size(), 0);
char buf[1024] = {0};
ssize_t s = recv(_sock, buf, sizeof(buf), 0);
if (s > 0)
{
buf[s] = 0;
std::cout << "server return " << buf << std::endl;
}
else if (s == 0)
{
close(_sock);
std::cout << "server quit" << std::endl;
break;
}
else
{
close(_sock);
std::cerr << "recv error " << strerror(errno) << std::endl;
break;
}
}
}
private:
int _sock;
std::string _sip;
uint16_t _sport;
};TCP服务端
class tcp_server
{
public:
using func_t = std::function<std::string(const std::string&)>;
public:
tcp_server(func_t func, uint16_t port)
: _listen_sock(0), _port(port), _quit(false), _func(func)
{}
~tcp_server() {
close(_listen_sock);
}
void init()
{
// 1. socket
_listen_sock = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
if (_listen_sock < 0)
exit(SOCKET_ERR);
INFO("socket success %d", _listen_sock);
// 2. bind
struct sockaddr_in local;
memset(&local, 0, sizeof(local));
local.sin_family = AF_INET;
local.sin_addr.s_addr = INADDR_ANY;
local.sin_port = htons(_port);
if (bind(_listen_sock, (struct sockaddr*)&local, sizeof(local)) < 0)
exit(BIND_ERR);
INFO("bind success");
// 3. listen
if (listen(_listen_sock, backlog) < 0)
exit(LISTEN_ERR);
INFO("listen success");
}
void start()
{
signal(SIGCHLD, SIG_IGN);
while (!_quit)
{
struct sockaddr_in peer;
socklen_t len = sizeof(peer);
int sock = accept(_listen_sock, (struct sockaddr*)&peer, &len);
if (sock < 0)
continue;
std::string cip = inet_ntoa(peer.sin_addr);
uint16_t cport = ntohs(peer.sin_port);
std::string cli = '['+cip+':'+std::to_string(cport)+']';
INFO("accept success sock %d %s", sock, cli.c_str());
//v1
service(sock, cli);
//v2
pid_t id = fork();
if (id < 0)
{
std::cerr << "fork failed" << std::endl;
close(sock);
continue;
}
else if (id == 0)
{
close(_listen_sock);
if (fork() > 0) exit(0); // 孤儿孙子进程提供服务,孤孙进程由操作系统负责回收
service(sock, cli);
close(sock);
exit(0);
}
else
{
close(sock); // hand it to childproc, must close it to save resources
pid_t res = waitpid(id, nullptr, 0);
if (res == id)
std::cout << "wait childproc success " << id << std::endl;
}
//v3
pthread_t tid;
thread_args* data = new thread_args(this, sock, cli);
pthread_create(&tid, nullptr, routine, data);
pthread_detach(tid);
std::thread th(&tcp_server::service, this, sock, cli);
th.detach();
//v4
task t(&tcp_server::service, this, sock, cli);
thread_pool<task>::get_instance()->push(t);
}
}
static void* routine(void* args)
{
thread_args* td = static_cast<thread_args*>(args);
td->ts->service(td->sock, td->cli);
delete td;
return nullptr;
}
void service(int sock, const std::string& cli)
{
char buf[1024] = {0};
ssize_t s = recv(sock, buf, sizeof(buf) - 1, 0);
if (s > 0) {
buf[s] = 0;
send(sock, buf, strlen(buf), 0);
}
else if (s == 0) {
INFO("%s quit, cancel service", cli.c_str());
break;
}
else {
ERROR("recv error %s", strerror(errno));
break;
}
close(sock);
}
private:
int _listen_sock;
uint16_t _port;
bool _quit;
};网络套接字编程的本质是利用系统调用从零编写应用层,不是使用应用层。